Bursitis Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Bursa?
Bursae (plural for bursa) are flattened, fluid-filled sacs that function as cushions between your bones and the muscles (deep bursae) or bones and tendons (superficial bursae). The sacs are comprised of connective tissue, just as muscles, tendons, ligaments and fascia are also made of connective tissue. Bursae are typically quite small and very thin; for an adult, the average diameter of a bursa approximately 4 cm.
A bursa will reduce friction and allow your soft tissue to slide over bone effortlessly during muscle contraction. Bursae are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes fluid that is rich in protein and collagen and act as the lubricant between areas in your body where friction (rubbing) is greatest.
These sacs form in areas where 2 surfaces in your body, most often where a bone and tendon or a bone and muscle, rub together during movement. When pressure or friction is too great, excess fluid can build up in the bursa sac causing inflammation. When a bursa becomes inflamed, moving the affected area becomes very painful and movement can be difficult. Any actions that put pressure on the inflamed bursa can increase irritation and cause further inflammation and pain.
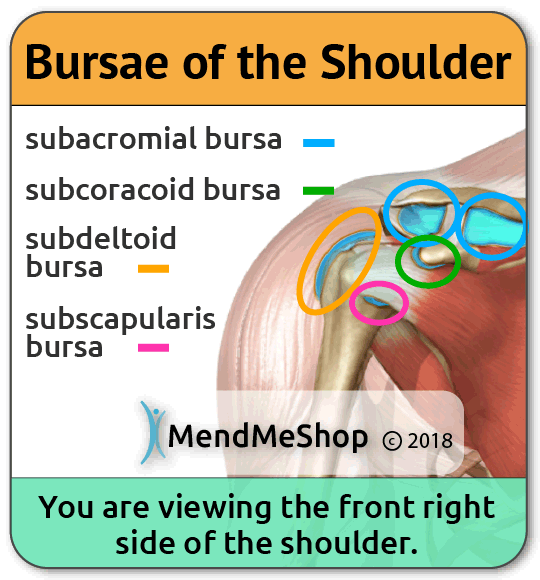
How Many Bursae Are In My Body?
There are approximately 160 bursae in our bodies, however, not everyone has the same number of bursae. Bursae can also vary in size from one person to the next and may become larger over time.
How Thick is a Healthy Bursa?
Average thickness of a healthy bursa is about 2 millimeters; knowing that some bursae can expand to the size of a plum should give you an indication of just how swollen they can get!
Why Does Bursitis Hurt So Much?
There are a LOT of nerve endings within a bursa, meaning bursae are quite sensitive - this why there is so much pain when a bursa becomes inflamed. When you have a lot of nerve endings in a sac that has swollen to multiples of its original thickness, you will definitely experience substantial pain.
What Types of Bursae Are There?
The medical community has generally established the following 3 types of bursae:
Deep Bursa / Synovial Bursa
Synovial bursae / Deep bursae are typically located near the synovial membrane of your joints. These bursae separate bare areas of bone from overlapping muscles. Deep Bursae develop in the womb.
Superficial Bursa / Subcutaneous Bursa
A Superficial Bursa separates bare areas of bone from skin or tendons to allow friction-less motion of your skin over the bone. An example of this can be found on the back of the elbow. Superficial Bursae develop within months to several years after birth.
Adventitious Bursa / Accidental Bursa
An Adventitious Bursa is a bursa that has formed in response to repeated pressure or stress over a bone. This is sometimes called an accidental bursa. The larger subcutaneous calcaneal bursa lies over top of the achilles tendon at the lower back of the heel where the tendon joins to the heel bone. This bursa develops as you age with the intent of protecting the tendon from friction at the back of the heel. It is not found in everyone and for this reason is termed an "adventitious" bursa. A bunion is another example of an adventitious bursa.
You Are Born With Some Bursae
Some bursae occur naturally and some occur as a result of excess rubbing in a particular area. These bursae form initially to protect the area from the minor trauma. Major bursae are located adjacent to tendons and muscles near larger joints, such as in the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. However, not all tendons have a bursa and they can also form in smaller joints like your toes.
Your bursae play an important role in leading a healthy, active life. When the bursae are not irritated and working properly, your joints move smoothly and painlessly.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is a condition that means your bursa has become inflamed. When pressure or friction on a bursa is too high, excess fluid can build up in the bursa sac and/or the the lining of the sac can thicken, causing inflammation and usually quite a lot of pain.
Normally, bursa are flat and contain very little fluid. An injured bursa however, is swollen with fluid and not so flat anymore.
How Long to Recover From Bursitis?
After undertaking conservative treatment options including rest, cases of acute bursitis recovery will typically take between 1 to 4 weeks to recover. If the underlying root cause has not been determined and dealt with however, bursitis can last months and even years.
Generally Speaking, What is the Best Way to Avoid Getting Bursitis?
Bursitis is best avoided by staying in shape, taking frequent breaks from repetitive or laborious tasks and cushioning joints if on them for long periods (ie. kneepads for gardening).
What Causes Bursitis?
Bursitis is most often caused by repetitive, minor impact on the area, or from a sudden, more serious injury. Stress, overuse, injury, or prolonged pressure on a bone can cause trauma to the soft tissue in a joint including the bursa. Injury to the bursa can result in widening of the blood vessels in the sac. This allows foreign fluids, blood and proteins to enter the bursa. When this occurs, the bursa reacts by swelling and you experience pain in the joint, especially when pressure is applied and during movement. These symptoms will continue until the fluid and/or proteins leave the bursa or they are broken down.

Some high risk activities for bursitis include overuse in areas such as gardening, raking, carpentry, shoveling, painting, scrubbing, tennis, golf, skiing, throwing, and pitching
Bursitis Caused By Acute Trauma
Acute trauma bursitis refers to bursitis caused by a direct blow to or twisting of the joint. For example, something as simple as an awkward fall may cause you to bang your hip or elbow, or you might bang twist your knee or ankle causing the bursa to be pinched. These types of injuries can cause serosanguineous discharge, a fluid composed of serum and blood, to leak into the bursa.
Serosanguineous fluid causes irritation and inflammation in the bursa and surrounding area resulting in pain and swelling.
Symptoms of acute bursitis are redness, tenderness of the joint, swelling & pain. Tenderness and pain will usually increase when you push on the bursa. If the bursitis is recent, redness and tenderness may take a few hours or a few days to appear.
Bursitis Caused By Chronic Trauma
This refers to repeated minor injuries to the bursa that occurs in one spot over time. It can be caused by repetitive motion, prolonged pressure on a joint, or an abnormality in the body that causes excess friction. With repeated injury, the bursa becomes irritated and thickens over time.
Working in a profession or enjoying a hobby that requires repetitive motion puts you at an increased risk of developing bursitis. For example hip bursitis is common in runners, shoulder bursitis in baseball players and painters, and elbow bursitis is often suffered by those who enjoy a frequent game of darts. As you repeat the same motion the bursa becomes over worked, irritated and eventually inflamed.

Wear and tear due to prolonged pressure on a joint can also cause bursitis. For example, resting your elbows on a table can cause olecranon bursitis (also known as student's elbow) or sitting on a hard surface for extended time periods can cause ischial bursitis (also known as weaver's or tailor's bottom). You may experience prepatellar bursitis (also known as housemaid's knee) if you are a carpet or tile layer or a gardener. Similarly, figures skaters or women wearing improper footwear are at risk of developing retrocalcaneal bursitis or Achilles bursitis. This type of bursa trauma usually occurs in athletes who overuse a joint or during middle age as wear and tear over the years begins to take its toll on our joints.
Abnormalities in the body that can cause excess friction can also cause increased irritation in a bursa. An example of this would be a mineral deposit, such as calcium, in a joint that rubs against a tendon or muscle. Other situations that may cause irregular friction in a joint are bone spurs, a loss of cartilage, or an abnormal bone growth such as a hooked acromion in the shoulder. When these obstructions exist, minor traumas within the joint occur over time, the bursa can become inflamed and the first signs of bursitis begin to develop; pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Bursitis Caused By Abnormal Depositis Due to Medical Conditions Such as Arthritis or Diabetes
Medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, scleroderma, gout, thyroid disease and diabetes can increase the risk of developing bursitis. These conditions can cause crystal deposits (gout) or calcific loose bodies (rheumatoid arthritis) to form within the joint causing irritation and inflammation in the bursa and surrounding tissue. For example, bursitis is common in people with gout because of their inability to properly break down uric acid which is a natural by-product of metabolism in the body. When it is not broken down properly, the excess acid begins to crystallize and settle in the joints.

Bursitis Caused By Infection
If your bursa becomes infected it is referred to as septic bursitis. Septic bursitis is usually caused by a bacteria know as staphylococcus epidermis (or staphylococcus aureus) that is commonly found on the surface of the skin. Bursae that are located just below the skin are more susceptible to infectious bursitis due to abrasions on the skin covering the bursa (the elbow is . With infectious bursitis the bursa fills with pus instead of blood or fluid and the area surrounding the bursa appears read and is very tender. Some septic bursitis stats: [1]
- Most cases of septic bursitis occur in males approximately 50 years of age
- Most cases of septic bursitis are due to repetitive trauma related to occupational behaviors. Plumbers, carpenters, roofers, clergy, and athletes are commonly affected.
- The staphylococcus aureus bacteria is responsible for 80% to 90% of all cases
- Infection of the bursa happens most often from micro-trauma or direct puncture of the overlying skin causing subsequent infection. In some cases, punctures due to steriod injections (with the intent of providing relief from non-infectious bursitis) have caused infection.
- People that suffer from gout and inflammatory arthritis are at an increased risk of septic bursitis.
In situations where bursitis has developed due to infection (aka "septic bursitis") you MUST see a doctor for prescribed antibiotics and possibly drainage of the bursa.
Septic Bursitis / Infectious Bursitis

With infectious bursitis the bursa fills with pus instead of blood or fluid and the area surrounding the bursa appears read and is very tender. In the case of septic bursitis, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to fight the bacteria. Alternatively, the bursa may be drained every 3-5 days until the infection is resolved.
Septic bursitis occurs more frequently in men than women, with 85% of the cases appearing in the male population. People who have diabetes, alcoholism, certain kidney conditions, or are undergoing steroid treatments are at higher risk of contracting septic bursitis.
Septic bursitis is most common in knee joints and elbow joints as the bursae in these locations are close to the skin and most susceptible to bacterial invasion.
As with any infection, it is very important to see your doctor to receive treatment for septic bursitis - if left untreated, the infection may spread through the blood to other parts of the body and it can become life-threatening.
What Are The Most Common Bursitis Conditions?
The most common bursitis injuries are:
- Prepatellar Bursitis (housemaid's knee)
- Superficial Infrapatellar Bursitis (clergyman's knee)
- Trochanteric Bursitis (bursitis of the hip)
- Olecranon Bursitis (student's elbow)
- Subacromial Bursitis (shoulder bursitis).
What is Chronic Bursitis?
Chronic bursitis describes a condition of bursitis that has persisted over a long period of time. With the buildup of excess fluid in the bursa sac, the sac will eventually expand and grow larger to accomodate the excess fluid. Over some time, the bursa will have expanded; pressure is reduced and pain may be much less that what it once was. Basically, chronic bursitis describes a condition where your bursa has likely grown larger yet inflammation and pain is reduced. In some cases, the larger bursa sac can create secondary issues such as impingements or in the case of the back of the heel - discomfort and irritation when wearing shoes.
What is Calcified Bursitis?
If bursitis persists and is left untreated, calcium deposits can form within the bursae. These calcium deposits limit range of motion and can lead to a permanently stiff joint.
What Are Some Other Names for Bursitis?
Household names for various bursitis injuries include:
- Popeye's Elbow
- Miner's Elbow
- Weaver's Elbow
- Housemaid's Knee
- Hod-Carrier's Shoulders
- Dustman's Shoulders
- Student's Elbow
- Clergyman's Knee
A Few More Interesting Points About Bursitis:
- It is not uncommon for bursitis to be misdiagnosed as arthritis.
- If a lump is present in chronic bursitis cases, excision may be required.
- Incorrect posture at work or home and poor stretching or conditioning before exercise can also lead to bursitis.
- Bursitis is most often caused by repetitive, minor impact on the area, or from a sudden, more serious injury.
Product specialists are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday.
If any question or concern arises, call us or simply send us an email at any time (we check our emails constantly all throughout the day and night.. even on holidays!). We will respond as soon as possible.
North America Toll Free 1-866-237-9608
Outside North America +1-705-532-1671
FREE SHIPPING ON ALL PRODUCTS CURRENTLY ENABLED
Please be aware that this information is neither intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. All testimonials and comments reflect the real life experiences of individuals that used our products, however, individual results may vary. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider before using any of our outstanding products to make sure they are right for you and your condition or if you have any questions regarding a medical condition.
For more information, call us via: 1-866-237-9608 or send us an email. View our Privacy Policy.
The terms Inferno Wrap®, Freezie Wrap®, T-Shellz® and Mendmeshop.com® are registered trademarks of In.Genu Design Group Inc.
All images shown are exclusive Copyright© 2006 - 2025 AidMyBursa.com.
Sources:
1. Truong J, Mabrouk A, Ashurst JV. Septic Bursitis. [Updated 2022 Sep 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470331/